Bed Bugs are rapidly resurging and capturing the attention of many countries throughout the world.It is essential that accurate knowledge of bed bugs, their habits, biology, reproduction, effective treatments and prevention strategies will assist in reducing the incidence of bed bug infestations worldwide.
Bed bugs are widespread and have been found in houses, apartments, hotels, schools, hospitals, dormitories, airplanes, and movie theaters. They use their straw-like mouth parts to suck blood from warm-blooded animals such as humans, bats, and birds. Adults are oval-shaped, flattened front to back, and wingless. Bed bugs hatchlings are so small they can pass through a stitch-hole in a mattress. At maturity, they are 4-5 mm long and 1.5-3 mm wide. They are light brown when hungry but after a feeding on blood, their abdomen looks bright red, red-brown, or blackish. Bed bugs may be mistaken for small cockroaches but unlike cockroaches, which scavenge human food, bed bugs feed only on blood. They remain hidden during the day and actively feed at night. Their bites are painless but the bite wounds can be extremely itchy for days later. Adult female can lay up to 500 eggs in her life.

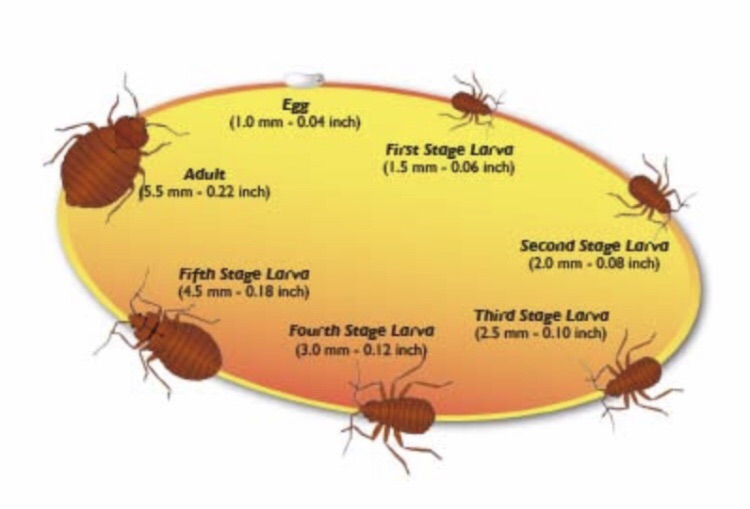
Bed bugs have three stages in their life cycle: egg, nymph, adult. Adult females lay eggs on rough dry surfaces near their hiding places, either singly or in small clusters. One to four weeks later, the nymphs hatch from the eggs and seek a host animal from which to feed. As nymphs eat and mature, they outgrow their skin, grow a new skin layer (exoskeleton) beneath it, and shed the old one, a process called molting. Following each molt, the nymph is a little larger. After the fifth growth-molt cycle, usually 4-6 weeks later, the bed bug reaches full size and is an adult. The process of changing body forms while maturing is called metamorphosis.
They are attracted to the blood of humans preferably, but will feed off of animals if need be. Bed Bugs are attracted by body temperature and CO2 the body release primarily thru breathing. They are also attracted to certain blood types, which explains why some family and friends in the same dwelling get bitten and others don’t. Bed Bugs often bite into human skin multiple times in search of the best blood flowing are for them to feed. Then they inject an anesthetic so they can feed uninterrupted for up to 10 minutes, and the go into hiding. They like to feed every 3-7 days if possible. Bed bugs can ingest seven times their own weight in blood, which would be the equivalent of an average-sized male drinking 120 gallons of liquid. If disturbed, alarmed, or crushed, they leave dark stains (fecal spots), often on sheets and bedding.
No bed bugs are resistant to heat and temperatures above 120 degrees will kill all bed bugs AND their eggs in a matter of minutes!
when done properly, the swirling high heat used to kill bed bugs effectively penetrates mattresses, box springs, furniture, and even walls to kill the bed bugs wherever they may be hiding! And since bed bugs are at first attracted to heat, they are less likely to scatter during the treatment.
with fans creating a “convection effect”, heat can penetrate and treat nearly all items in your home and there is no need to discard of expensive beds, furniture, electronics, or anything else that was infested prior to treatment.
Since the heat will penetrate most items using circulating air from fans, anyone performing the heat treatment will not need as much access into dressers, drawers, and other items as would typically be needed to do a chemical spray treatment.
Heat treatment does NOT require ANY toxic chemicals. For long lasting protection after a heat treatment you can choose to apply a non-toxic/food-grade “dust“ that will provide a residual effect and is safe for both pets and people.
